Brick veneer
A brick veneer, also known as a brick slip, is a thin layer of brick that is used aesthetically as a form of surface finish rather than structurally. Conventional brick walls typically support the structural loads of the building, whereas brick veneers are applied for decorative purposes.
They are generally formed from thin brick slips, which may be as little as 20 mm thick (compared to 102.5 mm for a standard brick). Brick veneers can be used for both indoor and outdoor applications and can be applied to almost any surface. A range of special brick slips are available for conditions such as corners, to continue the illusion that walls are constructed from full bricks.
For interior applications, such as around fireplaces, brick veneers may laid in a similar way to tiles. Mortar (or some other adhesive) is spread on the wall and the bricks are set into place on it, separated during drying by plastic spacers. Once bed mortar has set, the brick joints are pointed using more mortar. Other 'veneers' are available in rolls, as a form of three-dimensional wallpaper.
For exterior applications, the veneer may be laid in a similar way to internal applications, as a form of cladding. However, they may also be installed as a free-standing panels (often prefabricated off site, and sometimes including other components such as insulation), anchored back to the structural frame. This type of veneer is vertically self-supporting, but in multi-storey buildings, shelf angles may be used to provide a horizontal expansion joint, usually at the floor edges. This allows for expansion of the brick and potential shrinkage of the frame.
There are several advantages to using brick veneers:
- They are relatively easy and quick to install.
- They are not as heavy as other forms of masonry, which reduces structural loading.
- Cavities behind external brick veneers can aid insulation.
- They are durable and fire-resistant.
- They can achieve a wide range of decorative functions
- They require little maintenance.
Disadvantages include:
- They are more susceptible to damage as they are thinner than conventional brick walls.
- They do not contribute to structural integrity.
- They can be susceptible to water damage.
- Over time, the veneer will require re-pointing with new mortar.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
What they are, how they work and why they are popular in many countries.
Plastic, recycling and its symbol
Student competition winning, M.C.Esher inspired Möbius strip design symbolising continuity within a finite entity.
Do you take the lead in a circular construction economy?
Help us develop and expand this wiki as a resource for academia and industry alike.
Warm Homes Plan Workforce Taskforce
Risks of undermining UK’s energy transition due to lack of electrotechnical industry representation, says ECA.
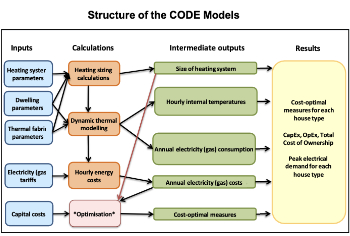
Cost Optimal Domestic Electrification CODE
Modelling retrofits only on costs that directly impact the consumer: upfront cost of equipment, energy costs and maintenance costs.
The Warm Homes Plan details released
What's new and what is not, with industry reactions.
Could AI and VR cause an increase the value of heritage?
The Orange book: 2026 Amendment 4 to BS 7671:2018
ECA welcomes IET and BSI content sign off.
How neural technologies could transform the design future
Enhancing legacy parametric engines, offering novel ways to explore solutions and generate geometry.
Key AI related terms to be aware of
With explanations from the UK government and other bodies.
From QS to further education teacher
Applying real world skills with the next generation.
A guide on how children can use LEGO to mirror real engineering processes.
Data infrastructure for next-generation materials science
Research Data Express to automate data processing and create AI-ready datasets for materials research.
Wired for the Future with ECA; powering skills and progress
ECA South Wales Business Day 2025, a day to remember.
AI for the conservation professional
A level of sophistication previously reserved for science fiction.
Biomass harvested in cycles of less than ten years.
An interview with the new CIAT President
Usman Yaqub BSc (Hons) PCIAT MFPWS.
Cost benefit model report of building safety regime in Wales
Proposed policy option costs for design and construction stage of the new building safety regime in Wales.
Do you receive our free biweekly newsletter?
If not you can sign up to receive it in your mailbox here.























Comments
There are many examples of brick slip failures from buildings constructed during the 1960s and 70s which have given slips a 'bad name'. Manufacturers of modern bricks slips are quick to point out that many lessons have been learned and that advances in adhesive and testing technologies have eliminated these fears. Despite this, an internal research study by materials specialist at Arup found that risks still exist around adhesively-bonded brick slip systems, and concludes by recommending the use of mechanically fixed (rather than adhesively fixed) systems only. A summary of the study is given here: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/brick-slip-cladding-systems-safe-alexis-harrison/